Science behind the Heart Wizard
Nutshell
Analyze and create programs for fitness, energy and performance levels for athletes and non athletes as well
Analyze your heart and create programs to improve your heart health
Analyze your Biological Age vs your Chronological Age. I, Dr. Paul, reversed my Biological age by 7 years in a 12 year period of time
Analyze and create programs for your Stress/Autonomic nervous system to balance it out
The Heart Wizard (TM) is a health and fitness assessment tool based on heart rate variability (HRV) analysis methods, which have became well-known and extremely popular for the past two decades.
While working on the Heart Wizard development project our professionals have studied tremendous amounts of research materials published in various scientific journals and have also conducted a series of their own research studies.
The Heart Wizard is a result of more than 20 years of hard work from a team of biomedical researchers, doctors, and software and hardware engineers.
The Heart Wizard includes a number of tools specifically designed to assess the various aspects of human health. Their combined use gives the ability to have a deep insight in saddle health changes.
The Health Snapshot ($45) test assesses the general health condition based on a dynamic evaluation of the Vagus nerve/autonomic nervous systems function.
The Vagus nerve/Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) is a mechanism which controls all of the body’s organs functions, such as the cardiovascular system, respiration, digestion, excretion, reproduction, body metabolism, immune system and many more. Depending on the ANS performance the body either functions normally or experiences functional problems.
At their early stages, many sicknesses can be linked to a disruption in performance of the Vagus nerve/ANS.
The Vagus nerve/autonomic nervous system consists of two branches – the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), which typically work as antagonists with regard to their effects on various organs and functions. For example, increased sympathetic activity causes blood pressure to rise and the heart to beat faster, while increased parasympathetic activity causes the blood pressure to drop and the heart to beat slower.
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the so-called general stress response, a generalized physiological reaction of the body to mobilize all of its resources for survival. This reaction is also known as the “fight or flight” response. During such reactions the increased sympathetic stimulation causes the heartbeat and blood pressure to increase, blood flow is redistributed from the skin and many internal organs to the skeletal muscles, airways and the pupils are dilated. The body is being prepared to fight or run away for survival.
The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for the relaxation response of the body, which is also known as the “rest and digest “phase. During this reaction the increased parasympathetic stimulation causes the heartbeat and blood pressure to decrease, blood flow is returned to the skin and internal organs, airways and pupils are constricted. This response is targeted to restore and conserve body’s energy for the future.
At rest both the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems are active with slight parasympathetic dominance. The actual balance between them is constantly changing in attempt to achieve equilibrium under the influence of all the internal and external stimuli.
Heart rate may serve as an integral indicator of such balance because it constantly changes beat-by-beat since it is under the influence of the complex regulatory mechanism controlled by the Vagus nerve/autonomic nervous system. This process is known as heart rate variability (HRV). For the past two decades the analysis of HRV has become one of the most important non-invasive methods of assessment of the Vagus nerve/autonomic nervous system function. It is accurate, reliable, reproducible, yet simple to measure and process. There are numerous research publications indicating that HRV analysis allows for assessing the level of activity of both sympathetic and parasympathetic functions, their balance and overall condition of the body’s internal mechanisms of regulation of many vital physiological processes.
The Health Snapshot test provides a simple procedure to quickly assess this balance condition while at rest. The algorithm of this assessment is based on the method of comparison of the results with normal ranges, widely used in medical practice. These normal ranges are built on the results of measures in the large population of healthy subjects.
Using this method our scientists have developed a unique algorithm of assessment of the levels of body’s activation energy (Sympathetic NS) and relaxation energy (Paraympathetic NS) as well as their balance based on the standard method of HRV analysis. Lowered levels of these parameters or their balance obtained in a single test can indicate that there is a problem with a body’s internal regulation caused by various negative factors such as fatigue, stress, emotions, etc.
If this imbalance continues repeatedly during a prolonged period of time, this could be a strong indicator of a saddle health problem, even though there are no obvious symptoms of any disease yet.
The Biological Age ($15) test allows for the measurement of one’s true biological age. Many would agree that it is hard to guess the age of a person. One person looks like a 40 year old but in reality, the age is 50. Another person may look 50 and it turns out that the age of the person is only 40. Calendar age reflects only the number of years that have passed since one’s birth. While biological age takes into account the quality and circumstances of an individual’s life as well as his or her personal health.
The Biological Age test is not a unique procedure from the scientific point of view. It is just one of the ways to present valid and well known scientific knowledge.
It is based on a simple method of evaluation of the baroreflex sensitivity, which can be assessed using a simple HRV analysis procedure. Baroreflex sensitivity is a measure of how quickly the blood pressure system can compensate for changes in conditions. There are many articles published in scientific journals showing that baroreflex sensitivity naturally degrades with age.
The baroreflex is involved when you stand up quickly and you feel dizzy. The baroreflex is a physiological mechanism responsible for the changing or heart rate in response to changes in systemic blood pressure. Rapid and dramatic drops in blood pressure may cause dangerous drops in blood supply to the vital organs such as the brain and thus lead to dizziness or even fainting. So the baroreflex swiftly increases the heart rate when blood pressure drops to compensate for the possible decrease in blood supply.
To measure the sensitivity of the baroreflex a deep paced breathing maneuver is used. During deep inhalation the chest is expanding and its internal pressure drops leading to slight drop in blood pressure because, large blood vessels inside the chest are stretched when the chest is expanded. The baroreflex causes the quick increase in heart rate as described above.
When deeply exhaling, the chest contracts so its internal pressure raises causing blood pressure to rise as well due to the shrinkage of large blood vessels in the chest. The baroreflex causes a quick decrease in heart rate as described above. This phenomenon is also known as respiratory sinus arrhythmia (RSA).
It was empirically found that the highest changes in heart rate induced by deep breathing happen when the breath rate is at about 6 breaths per minute.
Thus measuring the heart rate fluctuations caused by the deep breathing at a rate of 6 breaths per minute is a simple yet effective way to measure the baroreflex sensitivity. The less sensitive baroreflex is the lesser heart rate fluctuations happen.
Our scientists have conducted a special research study and selected specific HRV parameters, which appear to be the most significant in assessing baroreflex sensitivity. By analyzing the data of a large population of healthy individuals of different ages they created a mathematical model, which defines the relationship between these parameters and calendar age. Based on this model a unique algorithm of assessment of deviation of the biological age from calendar age was created.
The Fitness test ($35) measures the body’s current fitness level. What does that mean? It is no secret that an individual’s fitness can say a lot about ones health condition. Everyone can see the difference between someone who can easily run a few miles and someone who can’t walk even one hundred yards. The difference between the two has to do with their level of fitness. There are many tests that you can find on the Internet which will supposedly help you determine your level of fitness. Their main idea is always the same - do physical exercise such as squats or steps during a certain time interval, and then measure your heart rate. Unfortunately, such methods have some problems. First, it is hard to standardize such tests because one person can do more sit ups or step ups within the same interval of time. Second, measuring the heart rate after exercise accurately is difficult. And if you want to do it accurately, you must use a heart monitor device. The value of such tests is not great simply because of their inaccuracy. They were created a long time ago when computers didn't exist or were not affordable, yet were helpful for people to evaluate their fitness.
Now there are more accurate and effective methods of assessment of the body’s fitness level. One method is based on the analysis of the heart rate variability performed on the heart rate evaluated during a simple stand-up maneuver. The stand-up maneuver causes the heart rate to rise within the first 10-15 seconds because the blood pressure drops, due to the gravitational redistribution of the blood mass. Then, the cardiovascular system attempts to compensate from the orthostatic effect of standing up by constricting the peripheral blood vessels. As a result the blood pressure returns to its normal level and the heart rate drops. Many research studies have shown that the reaction of the cardiovascular system on the changing of the body’s posture, and the speed of its compensation or recovery, depends on the individual’s fitness level. The most indicative parameter of this test is a pattern of heart rate changes caused by the stand-up maneuver. The weaker and slower this reaction is, the less fit the body and, the more susceptible it is to physical exertions, which means a lower level of fitness.
Our scientists have analyzed a vast amount of research data on the subject of fitness assessment as well as conducted our own research on volunteers ranging from top athletes of national sports teams to ordinary people not capable to withstand even light physical exercise. Using this research data we developed our own algorithm for assessment of the fitness level based on the analysis of patterns of heart rate variability caused by the stand-up maneuver. This algorithm assesses one’s fitness level on two different scales – absolute and age-related. The absolute scale compares your fitness level with top athletes regardless of your age. This is a good way to see how competitive you are. However, it is not always a good way to assess fitness. For instance, a 50-years old male being in good health and athletic shape is not able to compete with a 20-years old top athlete no matter how well he is. However, for his own age he is in excellent shape and has high fitness level. These specifics are taken into account in our Fitness test. This approach gives complete full picture of one’s ability to withstand physical exertions.
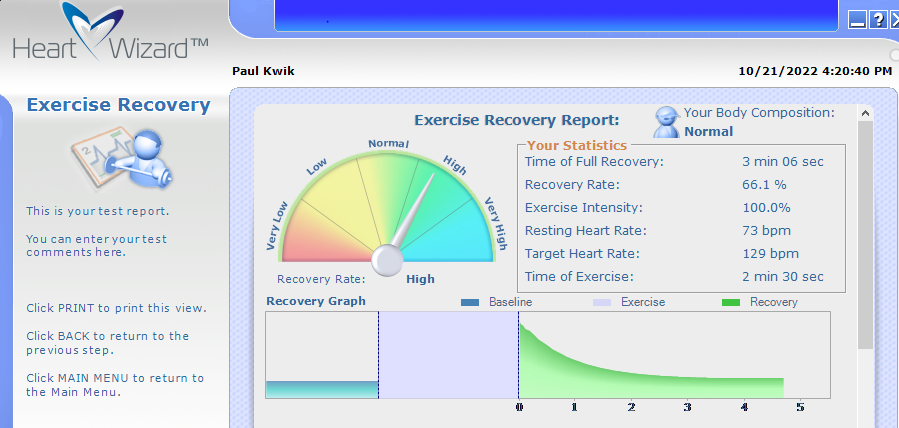
The Exercise Recovery ($65) test is a more in-depth way to assess one’s ability for optimal recovery after physical exercise. Optimal recovery means that the body achieves the same physiological conditioner level that it had before doing a test exercise. This recovery process occurs in a very efficient way. The quicker the recovery to baseline occurs the more efficient your organism is capable of handling physical challenges.
The following physiological processes occur in the body during exercise. Physical exertion causes increased activity of the skeletal muscles and their energy consumption. The energy is released from the utilization of nutrients in the presence of oxygen. The higher energy release, this means, the more oxygen that must be delivered to the muscle cells. To provide for the increased oxygen consumption the body increases the volume and rate of breathing. Heart rate and stroke volume are also increased to increase oxygen transport to the muscles. All these physiological processes are controlled by the Vagus nerve/autonomic nervous system. Thus the level of performance of the Vagus nerve/autonomic and cardiovascular systems determines the body’s ability to endure significant physical exertions. This level is also known as a level of cardiovascular fitness.
There are many different methods or ways assess cardiovascular fitness. The most reliable and accurate way to do this is to measure the maximum oxygen uptake (VO2 max). However this test requires very expensive equipment and a highly trained specialist is required to perform this test and interpret its results. Thus, the most efficient way to assess cardiovascular fitness of ordinary people is to the use heart rate recovery test. There are many research publications showing a high correlation of these two methods for cardiovascular fitness assessment.
I love this fitness test for the following reason: Its gives me a plan of action and motivates me.
Here are my results:
The most informative indicators of Heart Rate Recovery are the level of heart rate increase caused by a dosed physical exertion and the speed of the heart rate recovery after the exertion ceases. These indicators are the result of a dynamic interaction of the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the Vagus nerve/autonomic nervous system. When physical exertion begins, the sympathetic tonus increases significantly while parasympathetic tonus decreases to allow the sympathetic nervous system to quickly take control. When exercise is over, the parasympathetic nervous system immediately shoots in its full power to boost the recovery processes as the sympathetic tonus is slowly and gradually decreased. The effectiveness of the Vagus nerve/autonomic regulation depends on the intensity of the physical exertion and individual’s fitness level.
The main algorithm used in the Exercise Recovery test is based on well-known methods described in many published research materials. One of the key indicators assessed in this test is the Recovery Rate. The recovery rate shows how significantly the heart rate drops within the first minute of recovery (after the test physical activity ceases). The higher this parameter is the faster the recovery occurs.
We have also added calculation of exercise intensity to make the test results more comparable between tests. If this parameter is significantly lower than 100% then physical exertion is considered insufficient to challenge the recovery mechanism, so the Recovery Rate value cannot be considered as confident. So it is important when doing this test to raise your exercise intensity level to near 100% effort for a good assessment.
The Stress Sweeper ($45) provides a training tool that will help in reducing the stress effects on human organism.
The Stress Monitor provides a way to continuously measure and monitor the body’s stress level.
Stress is an important aspect when it comes to looking at ones health in general. There are many negative factors that affect our life every day, which causes our body to generate a stress response. Stressful episodes may be short or long. Our exposure to stress causing factors (stressors) is inevitable but, in many cases they are not significant and their effect is relatively harmless. Only very frequent or extremely strong stressors may exhaust the human body and trigger a developing health problem.
Regardless of the type of stressor (emotional, physical or their combination) the body’s physiological reaction has common traits. All physiological processes happening in the body during stress are well-studied and described in the literature.
Under the influence of a stressor a sustained focus of excitation is formed in the brain cortex which begins dominating all the body’s functions. This reaction initiates a chain reaction to prepare the body for a “fight or flight” response. It ignites a sequence of biochemical reactions throwing stress hormones into the bloodstream. They cause an increase in heartbeat, blood pressure, blood sugar level and speed up metabolic processes to increase energy production. As a result of this, the body is ready to fight for survival. If the effects of the stressors remain sustained, an excitation in the brain cortex persists and stress hormones keep being released into bloodstream.
This physiological mechanism of stress response has been developed by the nature in humans and other animals to survive. However, humans in the modern world do not use their muscular power in stressful situation so a natural stress response does not occur as it was designed by evolution. Therefore, the consistent stress level does not get released and instead, the problems are internalized. Good rest and relaxation now would work much better to resolve stress than the initiation of a typical “fight or flight” response. However, our body acts like it was meant to by nature so stress hormones circulate in the bloodstream keeping the body’s organs and functions in an agitated state.
The natural mechanism of stress was developed by evolution as a short-term protective measure. If the effect of the stressor remains for a long time, the stress mechanism goes into exhaustion phase. It drains all reserves of energy, vitamins and minerals, which leads to lowering body functions responsible for healthy stress reaction, causing extreme fatigue and can even trigger developing various stress related health problems, such as cardiovascular, neurological, autoimmune diseases, cancer, asthma, digestive problems and many more. It has been found that up to 80% of health problems are stress related. It is also found that the first most likely victim of unresolved chronic stress is the immune system, failure of which leads to colds and various inflammations. That is why having information about stress levels is extremely important in one’s everyday life to maintain good health.
The Stress Monitor is not unique from scientific point of view. Elevated stress level can be detected based on known typical reactions to stressors such as:
1) increased salivation and sweating;
2) decreased skin temperature;
3) increased heart rate, stroke volume and blood pressure.
The first type of reaction is used in galvanic skin response (GSR) devices, which measure skin conductance dynamically changing under effect of stress.
The second type of reaction is used in so-called stress cards or mood rings. These devices have embedded liquid crystals, which change their color based on skin temperature when are in contact with the skin.
However these two types of stress measurement have significant disadvantage. They significantly depend on ambient temperature. Besides, it is virtually impossible to build a calibrated scale well representing stress level because both skin temperature and galvanic skin response significantly vary from person to person. They can be used to assess the degree of change of body’s reaction compared to their initial baseline level but not to assess the level of stress.
Using the reaction of the cardiovascular system to stress is the most effective approach to evaluate stress levels. The Stress Monitor utilizes this approach. Our scientists have developed a unique algorithm based on a mathematical model of the individual stress level caused by any physical or psycho-emotional factors. This algorithm is based on specific analysis of heart rate variability of the cardiac intervals recorded for a short period of time or continuously. The algorithm contains special means for automatic adjustment of its performance to establish a method of self-learning and increasing its performance by taking into account individual physiological properties.
Do Your Own Research. Tons of info on “PubMed”
Copyright Material
Used with permission from Advanced Wellness Solutions